

Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
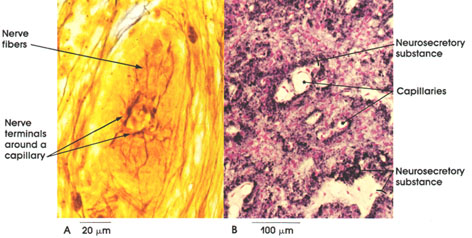
A. Pig, 10% formalin, Ranson's method, 500 x.
B. Rat, Helly's fluid, Gomori's chrom alum
hematoxylin and phloxine stains, 162 x.
The posterior lobe of the hypophysis, the neurohypophysis, is composed of nerve fibers that arise in the hypothalamus. Their cell bodies lie in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei. In A, nerve fibers and their pericapillary terminations are shown. In B, the method used selectively demonstrates neurosecretory material located in the axons. Note the abundance of blood vessels and the stained neurosecretory material surrounding the pericapillary spaces. It is believed that the nerve terminals release oxytocin and vasopressin into the blood stream. These two hormones are polypepticles. Oxytocin causes the smooth muscle fibers of the uterus to contract, a function essential for parturition, and can be used clinically to induce labor. Oxytocin also causes the myoepithelial cells of the mammary gland to contract, bringing about the flow of milk from the gland.
Vasopressin or antidiuretic hormone (ADH) raises blood pressure by acting on arterial blood vessels, stimulates the adrenal cortex, and increases the permeability of the distal and collecting tubules of the kidneys. This increases water reabsorption from the glomerular filtrate, inhibiting an abnormally large flow of urine (diuresis) and resulting in the formation of a urine hypertonic with respect to blood plasma.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2024 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/