

Granulocytes
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
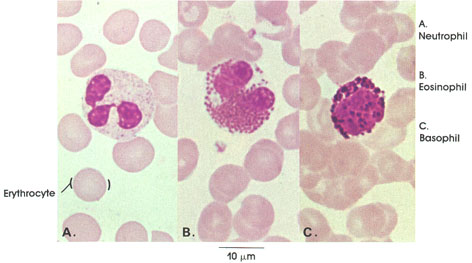
Human, air-dried blood smear, Wright's stain, 1416 x.
Erythrocyte: Usually biconcave and circular outline, devoid of a nucleus. Number in man varies between 5 and 5.5 million per cubic mm of blood. Erythrocytes carry oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs.
Neutrophil: Compare sizes of the neutrophil and the erythrocyte. Lobulated nucleus, individual lobes connected by thin bridges. Cell type-specific cytoplasmic granules are small. Neutrophils constitute 40 to 75 per cent of the total white blood cell count. The number of neutrophils increases in inflammation, and they act as the first line of defense against invading pyogenic organisms.
Eosinophil: Nucleus bilobed. Cell type-specific cytoplasmic granules are large and uniform in size and stain intensely red with acid dyes. They constitute 1 to 3 per cent of total white count and increase in number in allergic states and in parasitic infections.
Basophil: The nucleus is large but less lobulated than other white blood cells. Cell type-specific cytoplasmic granules are large and variable in size and have a strong affinity for basic dyes. They constitute 0.5 to 1 per cent of white count and are believed to synthesize the heparin and histamine found in circulating blood.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
Anatomy Atlases is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. 
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/