

Plate 10.186 Tooth (In Situ)
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
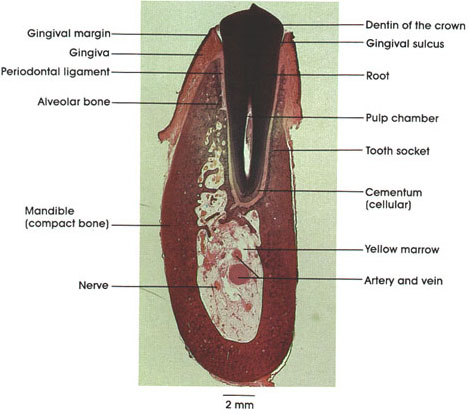
Cat, 10% formalin, decalcified, 4.6 x.
This in-situ decalcified tooth section illustrates many features of tooth structure. Realize that the enamel has been removed during the process of decalcification.
Note the crown (i.e., that part that projects above the gingiva) and root (i.e., that part located in the osseous alveolar socket).
Note the named parts of the gingiva: the superior free margin and the free gingival sulcus. The junctional epithelium of the gingiva ends by joining the cementurn and periodontal ligament. If the junction between the parts fails to remain sealed, infection of the periodontal tissues occurs (gingivitis), possibly leading to serious periodontal disease.
The alveolar bone (or tooth socket) functions as the insertion for periodontal ligament fibers, which join tooth to bone.
Human teeth never directly fuse with the alveolar bone, but rather, the tooth is suspended from the bone by the periodontal ligament.
Cementum, which forms the outer surface of the root, is composed of calcified collagenous fibrils, glycoproteins, and glycosaminoglycans.
Note the inferior alveolar nerve and blood vessels in the yellow (non-hematopoietic, fatty) bone marrow of the mandible.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
Anatomy Atlases is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. 
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/