

Atlas of Human Anatomy in Cross Section: Section 1. Head and Neck
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Jean J. Jew, M.D., and Paul
C. Reimann, B.S.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
|
Upper Left Quadrant |
Lower Left Quadrant |
Lower Right Quadrant |
Upper Right Quadrant |
|
1. Nasal cavity |
12. Styloid process |
30. Second cervical vertebra, dens of axis |
47. Parotid gland |
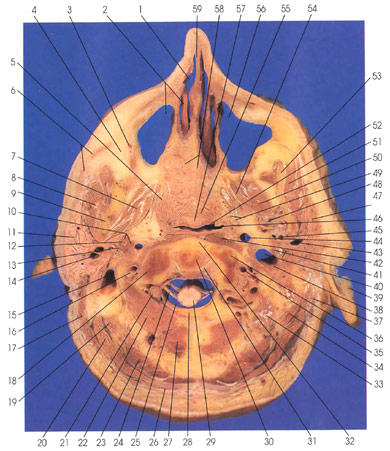
This section passes through the nasal cavity (1), maxillary sinuses (2, 56), uvula (57), pharynx (52), atlas (36), dens of axis (30), and the muscles of the occipital (17, 19, 20, 23, 26,27) and suboccipital (22, 33) regions. The section passes through the mandibular ramus (9, 53)
The parotid glands (11, 47) have their greatest extension in this section. The right parotid duct (6) is grazed in this cut.
The transverse atlantal ligament (cruciform ligament of atlas) (31) is seen separated from the dens by its articular capsule and space.
The second cervical dorsal root ganglion (21) is seen lying on the arch of the second cervical vertebra (axis).
The styloid process (12) and the stylopharyngeus muscle (10), which arises from the medial side of the base of the styloid process, are identified. The muscle is innervated by the ninth cranial nerve (glossopharyngeal). The stylohyoid (10) arises from the lateral and dorsal part of the base of the styloid process and is innervated by the seventh cranial nerve (facial). A third muscle, the styloglossus, arises from the front and lower end of the styloid process and is innervated by the twelfth cranial nerve (hypoglossal).
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2024 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/