

Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Paul M. Heidger,
Jr., Ph.D.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
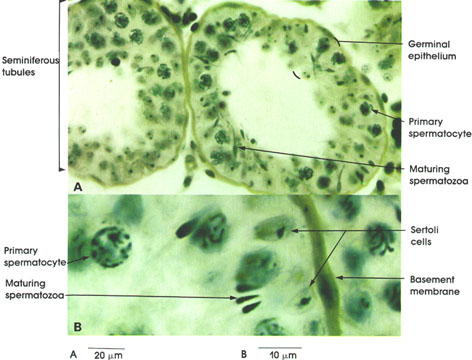
Rhesus monkey, Helly's fluid,
iron hematoxylin and orange G stains,
A. 162 x; B. 1416 x.
The germinal epithelium of the seminiferous tubules is composed of several layers of spermatogenic cells disposed between the basement membrane of the tubule and the lumen (see Plate 265).
Primary spermatocyte: Largest germ cell. Nuclei are large and vesicular and have condensed chromatin. Chromatin may appear as elongated threads.
Maturing spermatozoa: Mature germinal cell consisting of a head and a tail. The heads are in close association with Sertoli* cells, and the tails project into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule. Condensed nuclei forming the heads of spermatozoa contain a single set of chromosomes. Spermatozoa are the source of testicular hyaluronidase, an enzyme that may play a role in fertilization.
Sertoli Cell: These are supporting cells of the testicular epithelium. Tall columnar cells extend from the basement membrane to the lumen. These cells possess ovoid nuclei with a prominent nucleolus (seen here). Cell borders are not distinguished with light microscopy. Spermatozoa develop in intimate relation with the apical cytoplasmic processes of Sertoli cells.
Basement membrane: Surrounds seminiferous tubules, and is augmented by outer layers of connective tissue.
*Sertoli, 1842-1910, was an Italian histologist.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2025 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/