

Atlas of Human Anatomy in Cross Section: Section 6. Pelvis, Perineum, Hip, and Upper Thigh
Ronald A. Bergman, Ph.D., Adel K. Afifi, M.D., Jean J. Jew, M.D., and Paul
C. Reimann, B.S.
Peer Review Status: Externally Peer Reviewed
|
Upper Left Quadrant |
Lower Left Quadrant |
Lower Right Quadrant |
Upper Right Quadrant |
|
1. Mons pubis |
17. Medial femoral circumflex a. and v. and quadratus femoris m. |
26. Anus |
34. Iliopsoas m. |
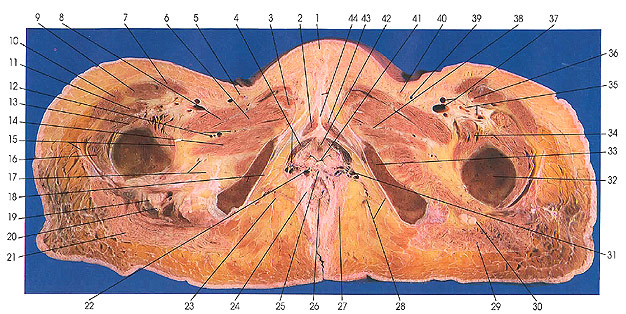
This section passes through the mons pubis (1), corpora cavernosa of the clitoris (2, 43), urethra (42), vagina (41), ischiocavernosus muscles (18, 28), femora (32), and anus (26).
The clitoris is located posterior to the pubic symphysis at the anterior end of the pudendal rim. It consists of a body, two crura, and a glans. The body is not free, like that of the penis, but is embedded in the connective tissue of the vulva. The body of the organ (44) is formed by the fusion of the two corpora cavernosa (2, 43), which differ from those of the penis only in size. It extends from the pubic arch anteriorly and posteriorly, being curved, and is about 2 to 2.5 cm in length. Unlike the penis, the third cavernous body is missing from the clitoris. At the inferior border of the pubis the two corpora cavernosa separate, bend sharply caudally, laterally, and dorsally, and follow the inferior borders of the inferior rami of the pubic bones (18, 33). These are the crura (legs) and they are covered by ischiocavernosus muscles (18, 28). A glans is attached to the distal end of the fused corpora cavernosa.
Next Page | Previous Page | Section Top | Title Page
Please send us comments by filling out our Comment Form.
All contents copyright © 1995-2025 the Author(s) and Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. All rights reserved.
"Anatomy Atlases", the Anatomy Atlases logo, and "A digital library of anatomy information" are all Trademarks of Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D.
Anatomy Atlases is funded in whole by Michael P. D'Alessandro, M.D. Advertising is not accepted.
Your personal information remains confidential and is not sold, leased, or given to any third party be they reliable or not.
The information contained in Anatomy Atlases is not a substitute for the medical care and advice of your physician. There may be variations in treatment that your physician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
URL: http://www.anatomyatlases.org/